Introduction
Schedule weighting is a project management method used to show the importance of different project activities within a determined schedule. Schedule weighting helps by effectively controlling and monitoring many factors including cost, complexity, resources, and duration.
Uses for schedule weighting:
- Helps to find and control the resources of a project.
- It also helps in identifying the activities that have the most impact on the results of any project.
- Used to improve and get a better accuracy of tracking a project.
Key Components of Schedule Weighting
- Distribution of activities
Usually, all projects include a breakdown from high-level activities to lower-level- activities. Control for these activities would happen if we divided these activities properly and more precisely for the sake of avoiding delays to our project.
- Weighting Criteria
- Cost: distributing weights based on the cost to ensure financial management.
- Complexity: deciding which activity will require skilled labor or a high level of management so that we give them higher weights.
- Resources: higher weights are given to the resources with intensive tasks.
- Duration: Longer durations usually take a higher weight but that can sometimes be misleading and not always correct.
Methods for Calculating Schedule Weight
- By Cost
To use the cost method, your schedule must be fully cost-loaded. This cost loading should represent the actual real work value that the work has been done with to avoid having any fake values. Weights are proportional to the costs that are for each activity.
Example:
When there is an activity A that costs 100,000, while the whole project costs 800,000. Therefore, to calculate the weight = (100,000/800,000) *100 = 12.5%
- By duration
The weight is calculated based on the planned schedule, unlike the cost method which was based on the actual schedule.
Activity weight= Activity duration/ (Total duration of the schedule)
This method is suitable for the basic schedules but it is not effective when the cost is high and change occurs a lot.
Example: Activity A duration = 60 days
The total duration of the project is 450 days
Therefore, the weight = (60/450) *100= 13.33%
- By resources:
The weights are calculated based on the hours of labor and the allocation of resources.
Example:
If Activity A requires 8 manhours/ day, While Activity B requires 10 manhours/ day, therefore Activity B would take a higher weight value since it needs a higher number of manhours.
- By complexity:
This method uses a pre-defined matrix for assigning the weights based on the risk along with the management and control. You create a matrix where you divide the activities into certain groups depending on their complexity and their ranking.
- My experience
It uses the lessons and the skills that were gained from similar projects to calculate the weights based on the estimated priorities of the tasks.
Example:
If you are assigned to design and do shop drawings for a unique structure, which you never executed a similar project before, you increase the weight of the WBS of the design and shop drawings due to that you will find difficulties in doing them for the first time. Using Primavera P6 for Weighting
Steps to implement weights inside Primavera P6
- Different custom fields: generate defined fields and order them in a way that you can estimate the activity weights.
- Weight assignment: you may use specific parameters, for example, “Budgeted Material” to automate the weights for the activity and make the process easier
- Global change: Start automatic calculation and estimation of weights for all the activities using special and customized formulas.
Example:
Activity A has budgeted hours equal to 200
Therefore: (200/total hours) *100,000 (total units’ weight)
Then you can export the data to Excel so that you can have a more advanced analysis and then re-import it into Primavera P6 for easy and seamless integration.
Steps to add weights in Primavera
- Open the required project where you need to assign weights
- Open the resources icon from the enterprise
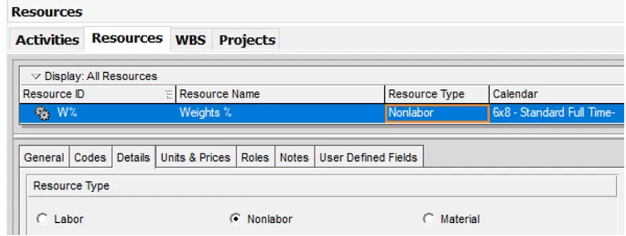
3. Add a new activity and choose if it is labor or nonlabor, along with assigning its weight, using any of the stated methods above.
4. You may also assign weights by changing the budgeted units of each activity as explained above in the article.
Best Practices in Schedule Weighting
- Project stakeholders usually engage together to define the criteria for the weights:
Essentially, all the stakeholders involved in a particular project must agree on the weights assigned to each of the project elements during the early phases of the project development.
- Review and revise weights whenever there are project changes:
Managing change is a very common issue in development projects because, for one or another reason, the scope, cost, or resources of a project change. This makes sure that when the project happens to it any changes that result in the formulation of new goals, the factors that should be prioritized in the project are consistent with the changes, keeping the main factors prioritized.
- During milestone reviews, update the major schedule changes:
Each day it is crucial to evaluate the progress made in the project and adjust weights and criteria to any important time shifts. For example, where tasks that used to be less important might have now taken longer time or are limited by resources, then they may need to be scaled up, and increase their weights based on the major change that happened.
- Avoid overcomplicating the design by strictly adhering to rigid rules and guidelines:
They should not lock the firm down in a rigid structure and allow for little creativity when it comes to the implementation of measures. An advantage of this approach is that it leaves the project team focused on the deliverables of the project and the needed goals to be reached while at the same time keeping the weighting process fair.
- Ensure criteria for weighting are clear to all stakeholders:
Stakeholders need to know what is happening and all of the updates at any time to remain interested and trust the project and organization.
Conclusion
Activity weight scheduling is an important technique when it comes to objectives and project control and monitoring. For instance, cost-based or resource-based weighting and the use of applications such as Primavera P6 can help a project manager avoid the distortion of the progress of the assessment and keep control over the decision-making processes during the project’s life cycle.