Introduction
Schedule Compression is used to shorten the overall project duration of a project schedule without changing the project’s scope. The Project Schedule is compressed when the project’s progress falls behind schedule. An appropriate schedule compression method is implemented to prepare a revised project schedule to mitigate the prevailing delays and ensure the project’s finish date per the original baseline schedule. The schedule compression methods are explained in this article.
Schedule Compression Methods
The commonly used schedule compression techniques are:
- Crashing
- Fast Tracking
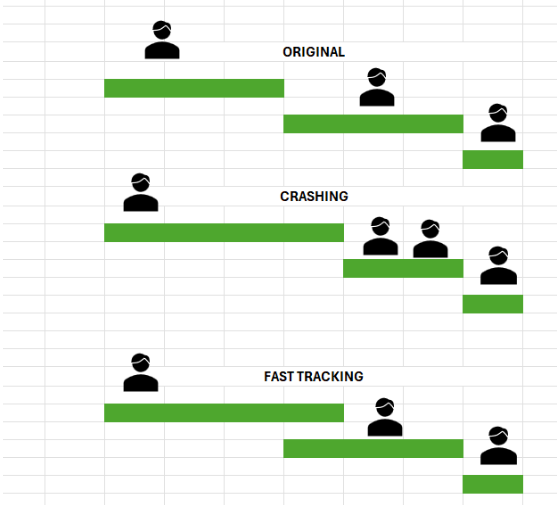
Crashing
Crashing is a schedule compression technique that reduces the project duration by decreasing the duration of critical activities. To do this, additional resources are assigned to the selected critical activities to reduce the duration of the respective activities. When the duration of these activities is reduced, the project completion date moves back, and the impact of the delay is mitigated. The planned sequence of activities and relationships between the activities are not changed in crashing. The advantages and disadvantages of this method are mentioned below.
Advantages of Crashing
Since the planned sequence of activities and the activity relationships are not changed in crashing, the probability of risk for quality issues is considerably reduced.
In crashing the timeline of key milestones and critical activities are maintained intact as per the baseline schedule to avoid delay penalties or liquidated damages. Crashing ensures timely project completion, stakeholders’ satisfaction, and the contractor’s reputation is preserved.
Disadvantages of Crashing
The budgeted project cost is increased due to additional allocation of resources which is a major disadvantage. Another disadvantage is the non-availability of required resources at the right time. If the necessary resources are not available as planned, it is impossible to implement the crashing method to reduce the delays.
The non-critical activities of the project schedule may turn into critical activities since the crashing method is implemented only for the critical activities of the project schedule. In that case, additional crashes are required. This is another disadvantage of crashing.
Fast Tracking
Fast Tracking is an alternative schedule compression method. Before applying this method, the critical path of the updated program is analyzed, and the critical activities are identified. Fast-tracking reduces the overall project duration by carrying out the critical activities simultaneously or providing necessary overlap between the selected critical activities.
The planned sequence of these activities is revisited to identify the soft logic in the project schedule. Soft logic is flexible activity relationships between independent activities. The selected critical activities for fast-tracking shall be carried out simultaneously or with reasonable overlap. The nature and quality of the activities are to be ensured while implementing this method.
Advantages of Fast Tracking
Additional resource deployment is not required during the implementation of fast-tracking, which is one of the main advantages of this technique. Therefore, additional spending on resource deployment shall be avoided.
Moreover, the idle time of resources is considerably reduced in fast-tracking since the resources are deployed for multiple activities simultaneously.
Resources are deployed on multiple activities concurrently in fast-tracking, reducing the idle time of resources.
The fast-tracking scheduling compression method ensures the project’s completion on time, and the delay penalties or liquidated damages shall be avoided.
Disadvantages of Fast Tracking
Since multiple activities are carried out simultaneously, the risk of quality issues and the probability of reworks are high in fast-tracking.
Moreover, additional staff may be required to supervise simultaneously progressing activities. The allocation of additional staff may lead to an increase in costs.
Conclusion:
The above-mentioned schedule compression methods are used to mitigate the impact of delays in a project schedule. A suitable method of compression of schedules shall be implemented based on the project requirements and budget constraints.
Crashing is desirable to maintain the original activity relationships in the baseline schedule and to reduce the risk of quality issues. Fast tracking is preferable to be cost-effective, but the risk of quality issues is higher.
A balanced approach, effective change control process, and proactive risk management are required to ensure successful compression.
Mastering scheduling methods and compression techniques can keep your projects on track. Need expert guidance? Contact us today for professional support!





