Introduction
In construction planning The Critical Path Method (CPM) is considered as one of the most used techniques. It is a project management tool used to calculate the overall project duration by calculating a series of connected activities. By the identification of the critical path, project managers can effectively prioritize these activities, allocate resources, and ensure successful project delivery as planned. CPM can be represented by a network diagram (activity on node) that outlines all tasks, their dependencies, durations, lags, floats, and the critical path.
What is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
The Critical Path Method (CPM) allows for the identification of critical activities that are needed for project completion and the development of the project schedule. It is a must to complete the project activities of the critical path on time according to the planned schedule to ensure the overall project’s successful closure. Delays in critical tasks will eventually delay the entire project.
CPM focuses on identifying the key tasks within a project’s timeline, understanding the interdependencies between tasks, and accurately estimating the duration of tasks and the overall project duration.
Having ineffective scheduling will eventually lead to cost overrun and delayed projects, CPM has become widely used because of its ability to prioritize tasks and simplify project planning processes. This can be achieved by dividing complex projects into smaller activities that are easy to control and track, and CPM provides insights about project flexibility and helps effective project management.
How does the CPM method work?
Regarding the implementation of critical path project management, it commences with four essential steps:
1. listing the Activities:
by breaking the project into WBS (work breakdown structure) and every WBS relates to the other WBS in a certain relationship and each WBS consists of a list of activities that are
2. Task Duration Calculation:
the duration is estimated according to many aspects like the method of work, expertise of the working team, resources, and as per contract.
3. Establishment of Task Dependencies:
Logic development or dependencies between tasks are identified according to the actual sequence of work, where the completion of one task impacts the start date of the succeeding task.
4. Milestone Noting:
Major project milestones and deliverables are recorded for future reference.
Once the necessary data is collected, we can represent the activities in many forms like Gantt chart, and activity on nodes, and obtain various charts. The critical path, the longest path of sequenced activities to project completion, is then identified. This allows for identifying critical activities and those with positive float, which can be delayed without extending the project duration. With this information, the project manager can have an overall look at the project and can make a proper decision regarding the starting or delaying of any activity.
Project Schedule:
| Activity | Duration | Predecessor(s) | Successor(s) |
| A | 5 | None | B, C |
| B | 3 | A | D, E |
| C | 4 | A | F |
| D | 6 | B | F |
| E | 2 | B | G |
| F | 3 | C, D | G |
| G | 4 | E, F | None |
Paths in the Project:
1.Path 1: A → B → D → F → G
2.Path 2: A → C → F → G
3.Path 3: A → B → E → G
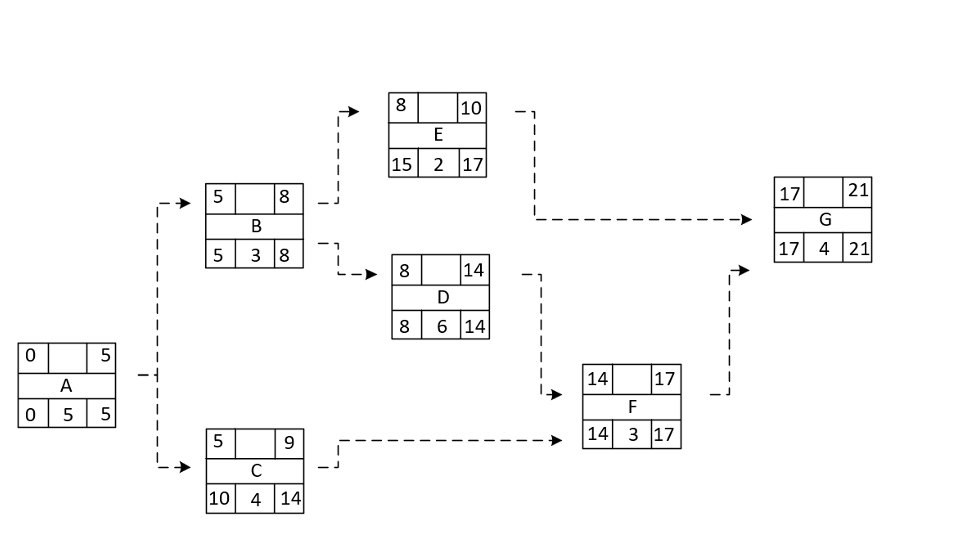
It can be represented using the activity on node method, as the following
Explanation:
● Activity A (5 days): the first and successors B & C.
● Activity B (3 days): Its Predecessor is Activity A, and successors D and E.
● Activity C (4 days): Its Predecessor is Activity A and successor F.
● Activity D (6 days): Its Predecessor is Activity B and successor F.
● Activity E (2 days): Its Predecessor is Activity B, and its successor is G.
● Activity F (3 days): Depends on Activities C and D, and successor G.
● Activity G (4 days): Depends on Activities E and F, with no successors.
This diagram shows the three paths forming the network:
A → B → D → F → G
A → C → F → G
● A → B → E → G
Critical Path Calculation
Let us calculate the earliest start (ES), earliest finish (EF), latest start (LS), and latest finish (LF) for each activity to determine the critical path.
Early Start (ES) and Early Finish (EF) Calculation
● A: ES = 0, EF = ES + Duration = 0 + 5 = 5
● B: ES = EF of A = 5, EF = ES + Duration = 5 + 3 = 8
● C: ES = EF of A = 5, EF = ES + Duration = 5 + 4 = 9
● D: ES = EF of B = 8, EF = ES + Duration = 8 + 6 = 14
● E: ES = EF of B = 8, EF = ES + Duration = 8 + 2 = 10
● F: ES = max (EF of C, EF of D) = max (9, 14) = 14, EF = ES + Duration = 14 + 3 = 17
● G: ES = max (EF of E, EF of F) = max (10, 17) = 17, EF = ES + Duration = 17 + 4 = 21
Late Start (LS) and Late Finish (LF) Calculation
● G: LF = EF = 21, LS = LF – Duration = 21 – 4 = 17
● F: LF = LS of G = 17, LS = LF – Duration = 17 – 3 = 14
● E: LF = min (LS of G) = 17, LS = LF – Duration = 17 – 2 = 15
● D: LF = LS of F = 14, LS = LF – Duration = 14 – 6 = 8
● C: LF = LS of F = 14, LS = LF – Duration = 14 – 4 = 10
● B: LF = min (LS of D, LS of E) = min (8, 15) = 8, LS = LF – Duration = 8 – 3 = 5
● A: LF = min (LS of B, LS of C) = min (5, 10) = 5, LS = LF – Duration = 5 – 5 = 0
Critical Path
The critical path is the sequence of activities that determines the minimum project duration. Activities on the critical path have zero slack (i.e., ES = LS and EF = LF).
For this project, the critical path is:
A -> B -> D -> F -> G
This critical path calculated the project’s total duration of 21 days.
Why use the CPM method?
1. The priority of tasks is particularly important in project management, and the critical path (CPM) helps project managers identify the most important activities that can significantly affect the duration of the project if it’s late. By focusing on these tasks, resources, and attention can be effectively allocated.
2. Analyzing the critical path in a project allows project managers to identify the tasks that can be delayed and for how long to prioritize critical activities leading to a successful on-time project closure.
3. The task dependencies used in CPM help with risk assessment by making it easier to evaluate the potential impact of missed deadlines on the planned goals or milestones of the project. This initiative-taking risk management approach enables taking corrective actions on time to mitigate risks and keep the project momentum.
4. A structured CPM framework is useful for measuring project progress against the planned schedule.
By comparing actual progress against the baseline schedule, project managers can identify discrepancies and deficiencies, allowing them to take corrective action immediately.
This ensures alignment with project goals and improves overall project control and performance
Mastering CPM scheduling is essential to keeping your projects on track—it’s the backbone of effective construction planning!
What are the CPM method weaknesses?
● Considering Activity durations are fixed:
The Critical Path Method (CPM) assumes that activity durations are fixed and predictable. However, many factors can have an impact on the activity’s duration, such as unexpected events (weather, political or legal constraints, material shortage, pandemics, etc.…), resource constraints or external dependencies. The CPM method may not be so flexible to deal with such uncertainties.
● Resource Constraint Complexity:
CPM does not account for resource constraints or resource leveling, which can lead to inefficient resource allocation at some parts of the project which leads to hiring and firing. This means that critical activities may not face resource constraints, while they might affect non-critical activities.
● 3-difficulty of Changing Priorities:
Difficult to change priorities: Once a project is in action and activities are scheduled, making changes will affect the entire project schedule. CPM is a project management system that lacks easy mechanisms to apply changes in priorities or scope during the project lifetime, making it less flexible to adapt to the needs of the project.
● Limited focus on non-critical activities:
Since CPM focuses mainly on identifying the critical path and critical activities, the non-critical activities are often overlooked. This limited attention to non-critical activities can lead to potential delays if they are not carefully considered or managed.
● Inability to Manage Resource Dependencies:
CPM assumes that every activity is solely dependent while there can be many activities that are dependent on certain resources, this eventually will lead to unrealistic scheduling and resource allocation
● Difficulty in Representing Complex Relationships:
CPM shines when it comes to representing simple project activities and their dependencies. However, its limitations for projects with complex networks make it challenging to interpret.
● Limited Integration with Risk Management:
CPM by its very nature does not incorporate risk management techniques such as Monte Carlo simulation or probabilistic scheduling. This can lead to project schedules that are not made while having the potential risks in mind resulting in a very optimistic/unrealistic scheduling.
The final conclusion is
That while CPM is a great tool for planning and scheduling projects and has become widely used in projects and supported by many tools and applications, it is important to recognize its shortcomings and complement it with other tools and techniques to address the complexities, risks, and uncertainties inherent in project management.





