Key Differences
As a project manager, you need to understand the difference between the critical and longest paths and their methodology. The main difference between the critical and longest paths is that the critical path focuses on time, while the longest focuses on activities.
Critical Path:
It is the activity path with the longest duration in the project, as it shows the minimum time required to finish the project.
- There is no project Deadline.
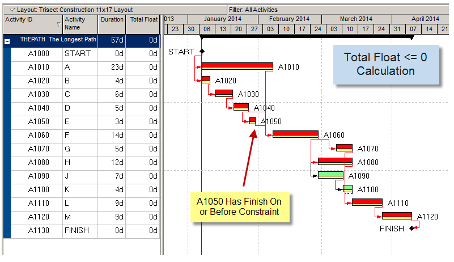
When the project has a constraint to finish on a specific date, you will note the appearance of the total float with -ve if the project is delayed or +ve values if the project leads which, removes the zero total float.
- There are no constraints.
Appearance of constraints in the project schedule can lead to critical activities and the total float value.
- There are no actuals.
Actuals applied to the project cannot show the zero float.
If any of the above conditions change, the critical path, or paths with the least total float could be near the critical path, Therefore the critical path could be more than one path.
Properties of critical path
- The shortest duration to complete the project.
- Total float = zero
- Any delay that happens to the critical path will extend the duration of the project.
When using CPM you can also schedule and manage your project through scheduling consultants.
Longest path:
Activities path that takes the longest time to complete
- The path where any changes happen from the plan will affect the project’s finish date.
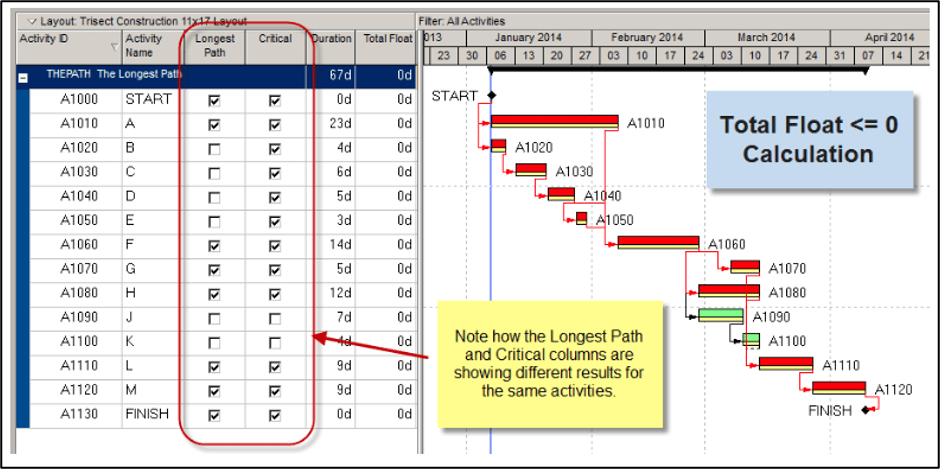
- The longest path is a critical path, but not all critical paths are the longest path.
- The schedule could have more than one critical path but only one longest path.
- Completion of the longest path activities leads to the project finishing on time.
Properties of the longest path
- The longest path is the longest duration of the project.
If the longest path is the critical path, therefore:
- Total float = zero
- Any delay that happens to the critical path will extend the duration of the project.
The overlapping between the two paths
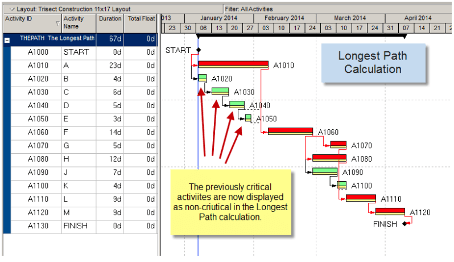
The path has zero total float when creating the baseline schedule with no constraints, actuals, or deadlines. Therefore, the path is the longest.
The variance between total float and the longest path is that if the total float is zero, then it is a critical activity which does not mean that the activity is in the longest path.
The determination of the critical path helps the project manager to implement the most critical task and ensure that the project stays on schedule, the longest path is the critical path while not all the critical path is the longest.
The difference between the two paths
In terms of project management, by using the critical path project managers can prioritize tasks and use resource allocation effectively, while by using the longest path project managers will understand which tasks require more resources and attention even if they are not critical.
Analyzing handling of task dependencies and constraints differently by using two paths
| Type of path | Critical Path | Longest path |
| As we identified above, the critical path analysis shows the path of activities that must be finished to minimize the overall duration of the project | As we identify above, the longest path analysis shows the path of activities that take the longest time to complete | |
| Task dependencies | Focus on task dependencies to determine the path as by analyzing dependencies between activities, the critical path is identified | Not the focus in determining the longest path as the longest path only aims to justify the longest duration regardless of any order |
| Constraints | Focus on constraints such as resources, deadlines, or any constraints that affect the project schedule | Do not focus on constraints as the critical path, as it focuses on identifying the activities that may affect the overall duration |
The Methodology
Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Define project activities and duration.
- Make the network diagram by using Diagramming or an activity-on-node diagram.
- Identify early start (ES), early finish (EF), late start (LS), and late finish (LF).
- Calculate the total float by using this equation.
The total float is the time that the activity can be delayed without affecting the project duration and if the total float is equal to zero, therefore, the critical path is the path that has zero float.
TF = LF – EF
Longest Path Method (LPM)
- Define project activities and duration.
- Make the network diagram by using Diagramming or an activity-on-node diagram.
- The longest path would be the path that has the longest total duration.
Primavera P6 Options:

Primavera p6 has a standard that the critical path is the path in which total float is equal to zero hours, you can change it easily by defining it.
you can change it easily by defining it.
|
Critical path equals total float = zero
|
Critical path equals the longest path |
 |
 |
Conclusion
Critical and longest paths have different impacts on project management, where the critical path helps to identify the best time to finish the project and the critical activities that could delay the whole project if any delay happens.
Hire us as a CPM Scheduling Expert for your next Project. Contact us today!
The longest path identifies the longest duration of the project, and choosing between them depends on the project requirements.
Leopard Projects Control offers in-depth resources on CPM scheduling, helping you navigate complex project timelines efficiently.