Introduction:
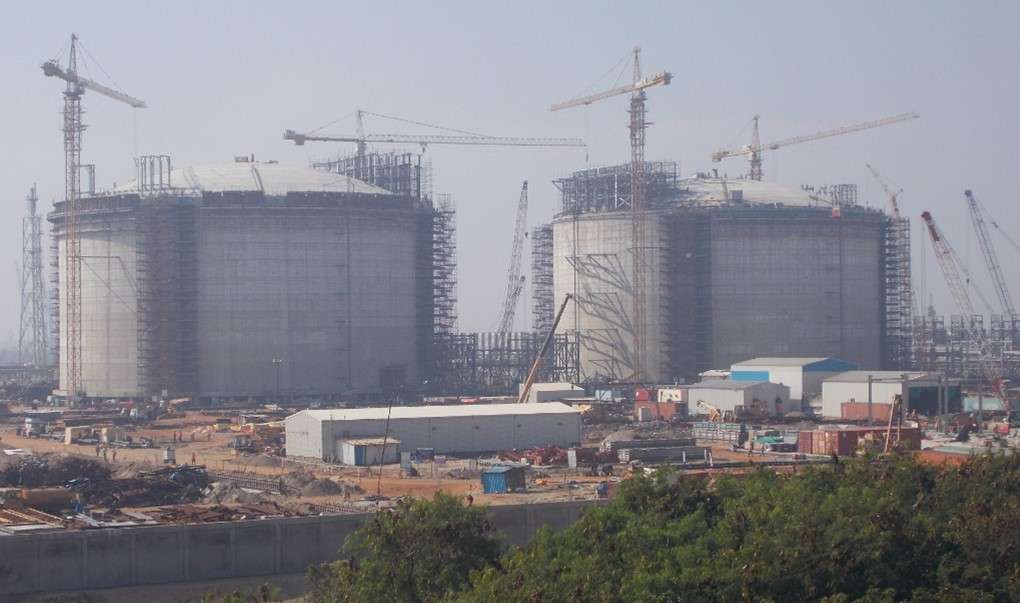

1 – An LNG tank during its construction
Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) is emerging as an important component of the global energy landscape, offering a cleaner and energy-efficient alternative to traditional fossil fuels. Delve into the significance of LNG Tanks and the Construction Sequence, exploring the key elements shaping this transformative energy landscape
LNG tanks or Liquefied Natural Gas tanks are specialized storage tanks that are designed to store natural gas in its liquid form. These tanks can be found in the ground, above ground, or in LNG carriers.
The most important characteristic of LNG tanks is the ability to store LNG at very low temperatures of -162 degrees Celsius (-260 degrees Fahrenheit) through a process called liquefaction. At these temperatures, natural gas changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state, becoming significantly denser and easier to transport and store.
LNG tanks are used for various purposes:
- Storage: LNG tanks are being utilised at production facilities and storage terminals to store large quantities of liquified natural gas. Tanks vary in size and capacity depending on the requirement.
- Transportation: LNG is often transported to long distances over sea, rail, or road. The specially designed LNG carriers transport the liquid from exporting terminals to importing terminals.
- Distribution: In some cases, LNG is transported to distribution points via trucks or railcars to consumers who are not connected to natural gas pipelines. These careers are insulated and designed to maintain the low temperatures of LNG during transit.
- LNG as Fuel: LNG is a clean burning fuel and hence is used for various applications including trucks, buses, ships, and some power plants.
Leopard Projects Control provides expert guidance and strategic oversight to optimize the construction schedule for LNG tank projects, ensuring timely and efficient project completion.
Typical Work Breakdown Structure in any LNG tank construction
A typical WBS followed in any LNG tank construction is outlined below:
- Early construction work
- Soil investigation
- Site office and temporary facilities
- Batching plant
- Fabrications at site
- Fabrication of anchor plates
- Corner liner anchor
- Secondary barrier shell top anchor
- Side liner anchor (lower)
- Side liner anchor (upper)
- Fabrication of liner plates
- Bottom liner plate
- Side liner plate (lower)
- Side liner plate (upper)
- Fabrication of roof
- Roof Skelton
- Roof plate
- Roof ring plate
- Fabrication of suspension deck
- Suspended deck beam
- Suspended deck plate
- Suspension rod
- Fabrication of inner tank
- Inner tank annular plate
- Inner tank shell stiffener
- Inner tank shell plate
- Inner tank bottom plate
- Fabrication of secondary barrier
- Secondary barrier annular plate
- Secondary barrier shell plate
- Secondary barrier bottom plate
- Fabrication of nozzles
- Manholes
- Nozzles
- Fabrication of structural steel works
- Structural steel works – mild steel
- Structural steel works – ss
- Fabrication of anchor plates
- Construction for tank
- Civil works
- Piling
- Pile Built-up
- Base slab
- Wall
- Roof
- Post-tensioning
- Structural steelwork
- Erection of structural steel
- Mechanical works
- Erection of anchor plates
- Erection of liner plates
- Pre-assembly of roof skeleton
- Erection of roof blocks
- Erection of suspension deck
- Erection of inner tank (9%)
- Erection of secondary barriers
- Erection of manhole/nozzle
- Insulation works
- Hydro test
- Machinery works
- Piping works
- Inner piping
- Outer piping
- Electrical works
- Power & control cable
- Cable tray & conduit
- Grounding & lightning
- Cathodic protection
- Instrumentation works
- Cable tray
- Cabling
- Loop testing
- Pre-commissioning
- Drying & N2 purge
- Commissioning assistance
- Civil works
Brief Construction sequence of LNG tanks
Site selection and preparation:
- The site of construction is to be chosen based on factors like proximity to LNG sources or consumption centers and local regulations.
- Site preparation includes all sorts of early civil works including grading, soil stabilisation, etc.
Foundation construction:
- The foundation consists of reinforced concrete footings (mostly, bored cast-in-situ pile foundation), followed by a base slab engineered to distribute the immense weight evenly.
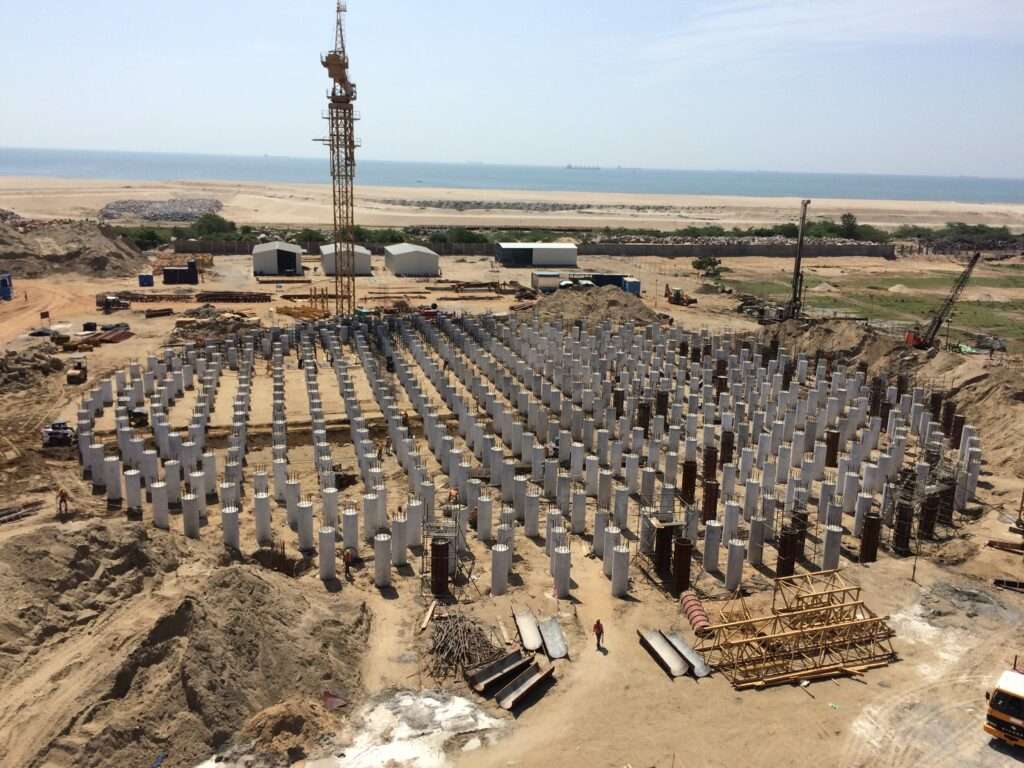

2 – Piles installation nearing completion
- The base slab construction shall be completed by segregating the slab into various segments
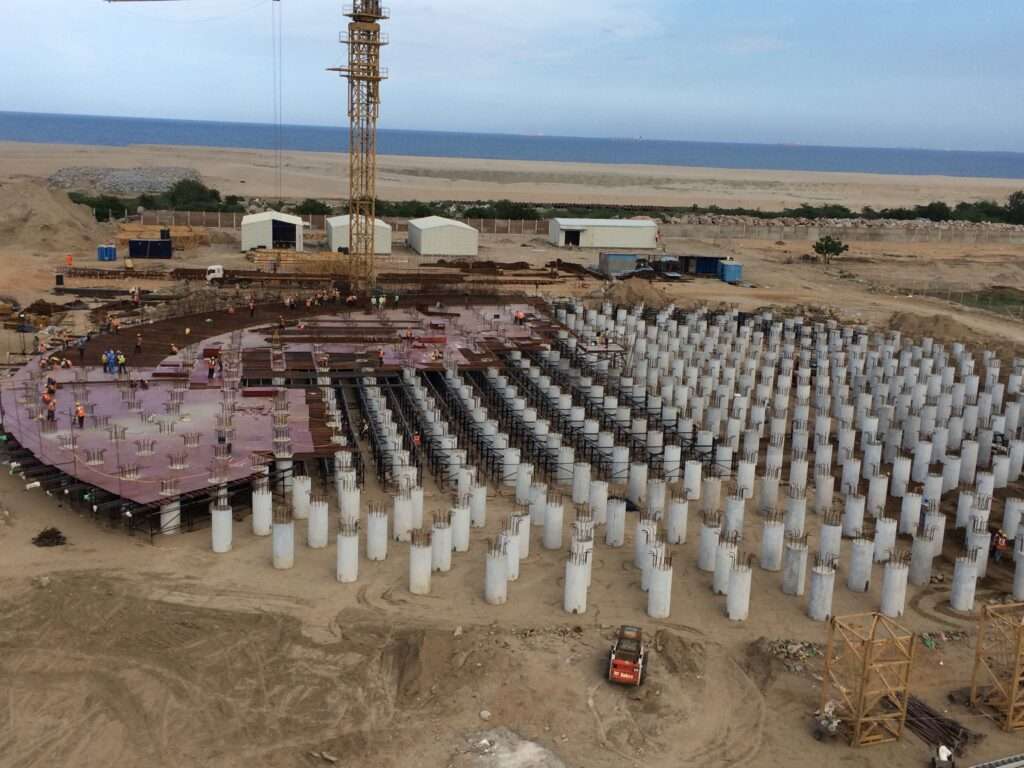

3 – Shuttering for baseslab in progress
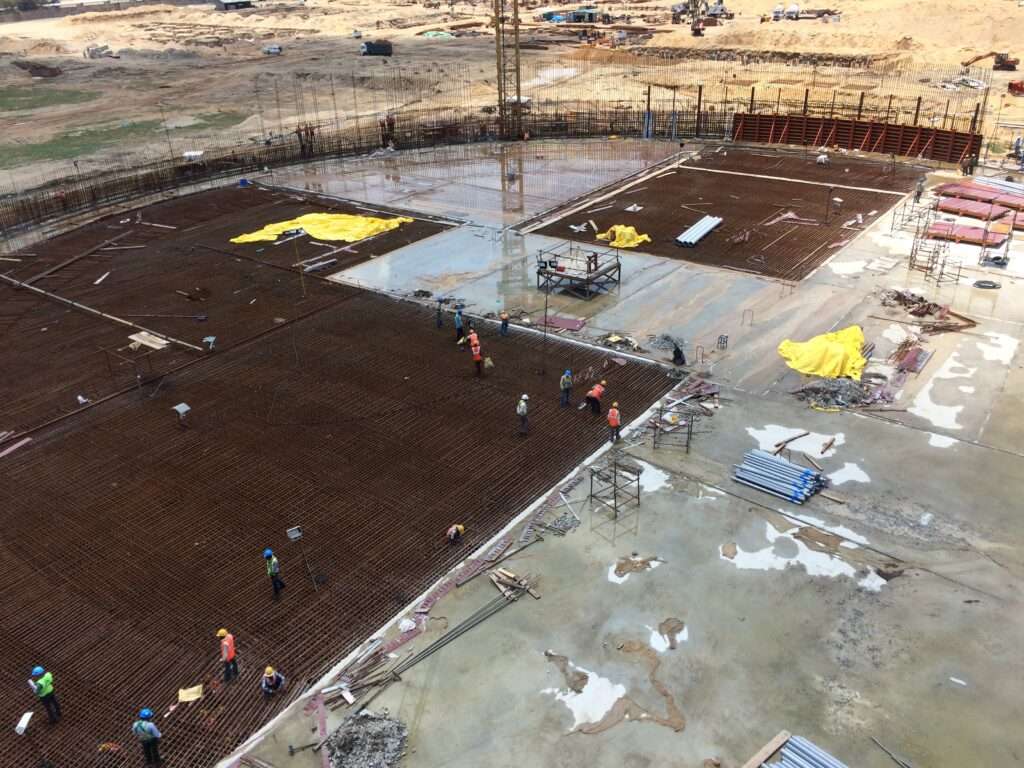

4 – Concreting in progress for baseslab
Fabrication works
- As a part of the mechanical works, the fabrication of the various liner plates and other structural steel works are initiated.
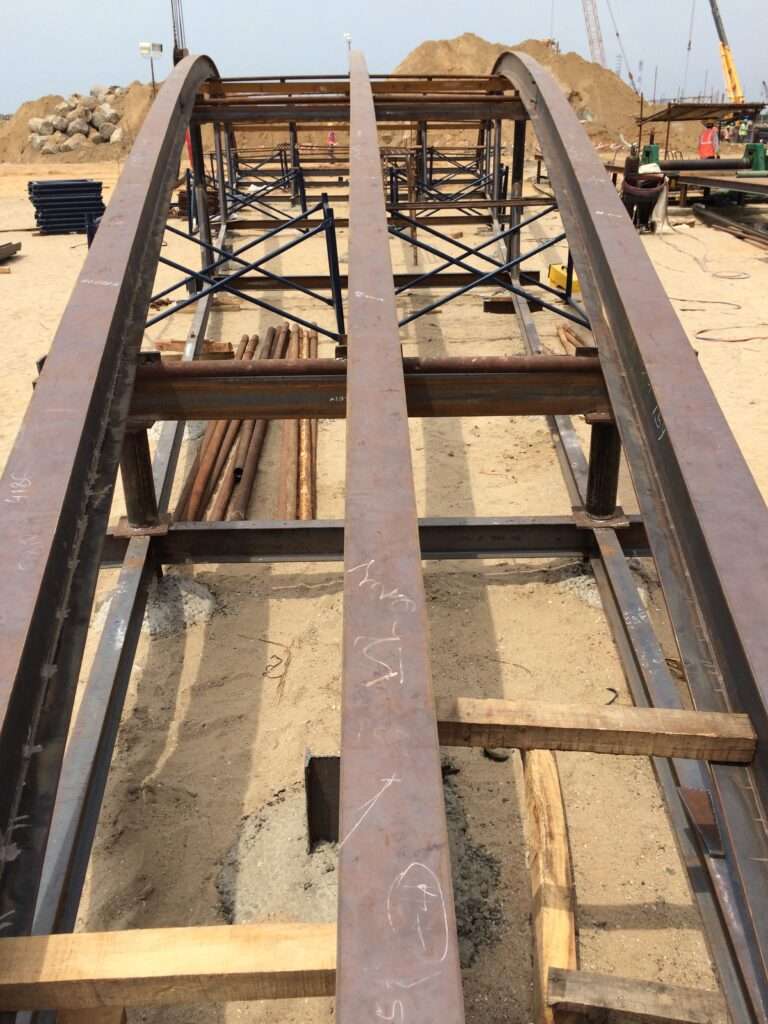

5 – Rafter fabrication
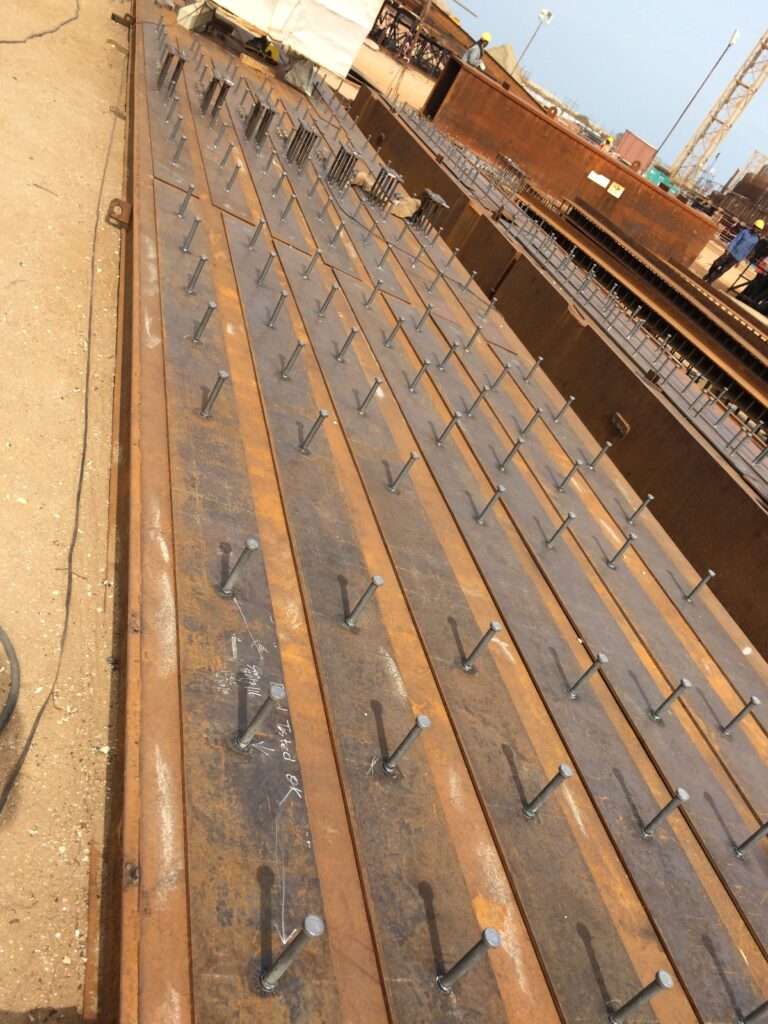

6 – Corner liner fabrication
Tank bottom and shell assembly:
- The corner ring is constructed before the base slab concreting and wall construction. This ensures the effective development of pre-stress between the wall and bottom slab. After the corner ring is cured, prestressing (PS) of the bottom slab and half of the wall is performed using tendons.
- The tank’s bottom and shell, which are made of high-grade steel are added onto the tank bottom and wall liners
- This activity would require precision welding to ensure the tank’s structural integrity and QA/QC measures are in place.
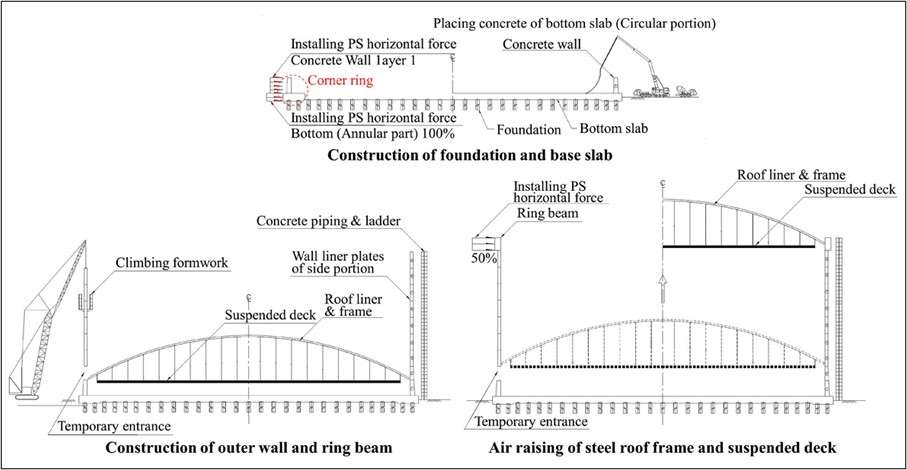
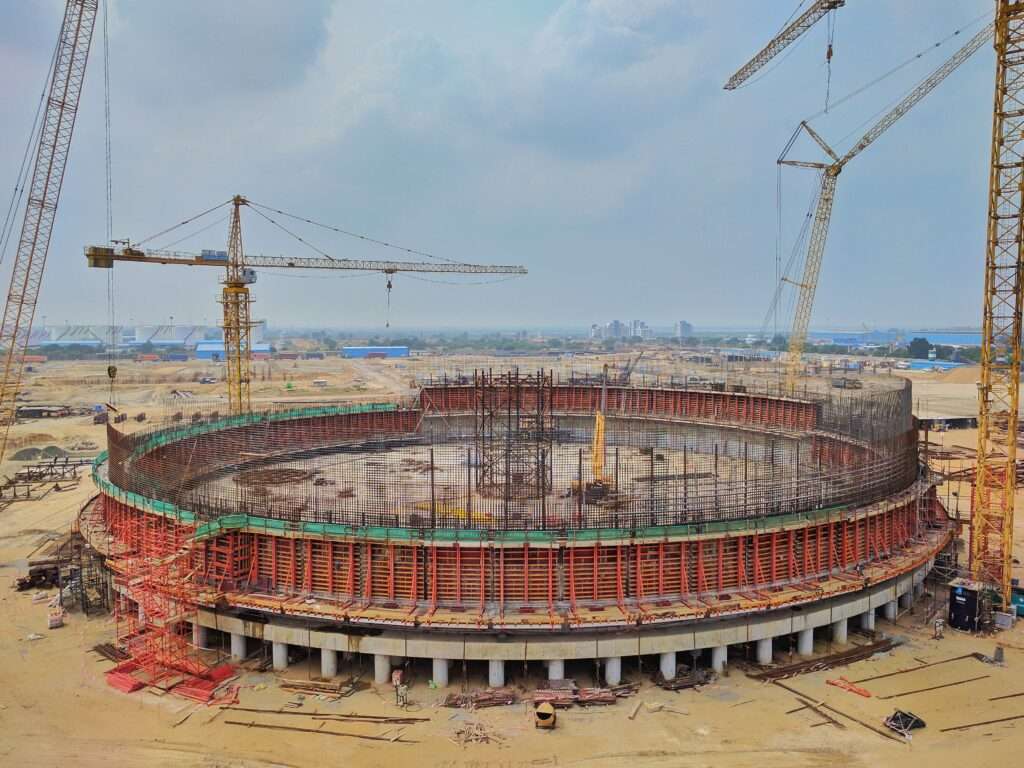
7 – Typical sequence of construction – Foundation, wall, ring beam, and suspended deck
Be sure to read our informative article on the impactful use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in construction projects.
Wall construction:
- The exterior wall of the tank is RCC (reinforced cement concrete) and the concreting of the same shall be with the help of a climbing formwork.

8 – Climbing formwork
- The PS tendons in the ring beam are installed in two steps. The initial half of PS tendon installation takes place before roof construction and installation of the latter part takes place after concrete roof construction.
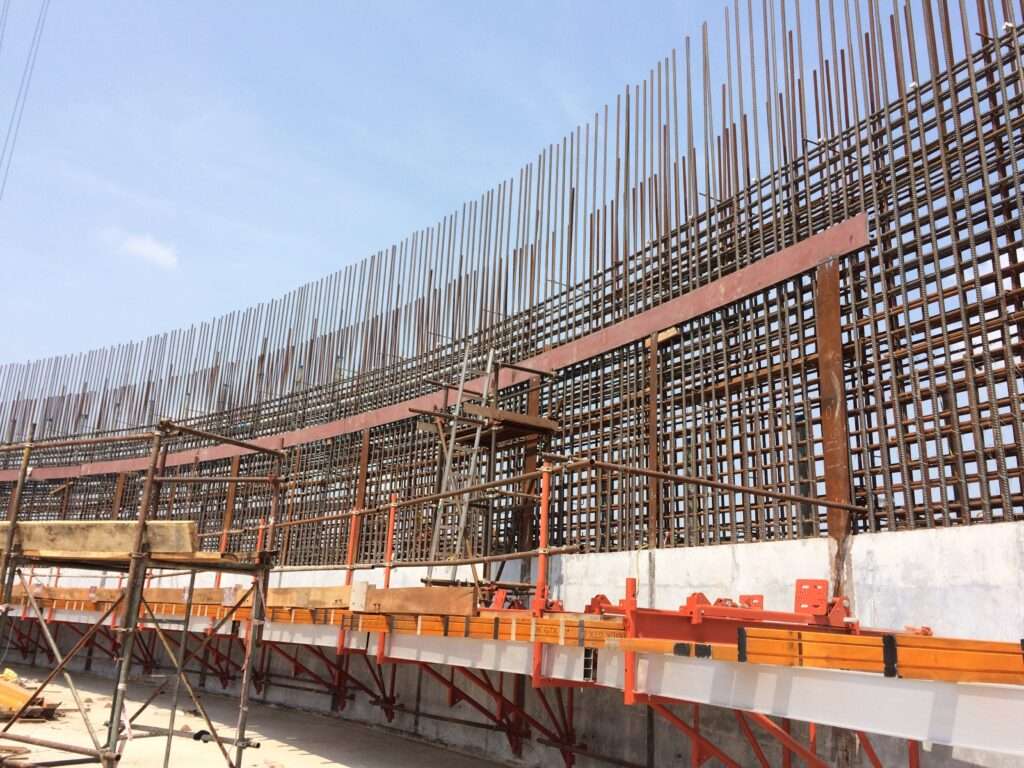

9 – Climbing Formwork
Insulation installation:
- To maintain the extremely low temperatures of LNG, insulation is provided to maintain the cryogenic state.
- Materials such as perlite or foam glass are applied to the tank’s inner surface
Roof installation
- The tank’s roof and the suspended deck are installed within the outer tank after the wall construction is complete. The roof is raised to the designated position through a process called Air Raising by using air pressure that is created by several blowers.
- Once the air-raising activity is completed, the dome roof is temporarily welded at the top of the RCC wall.
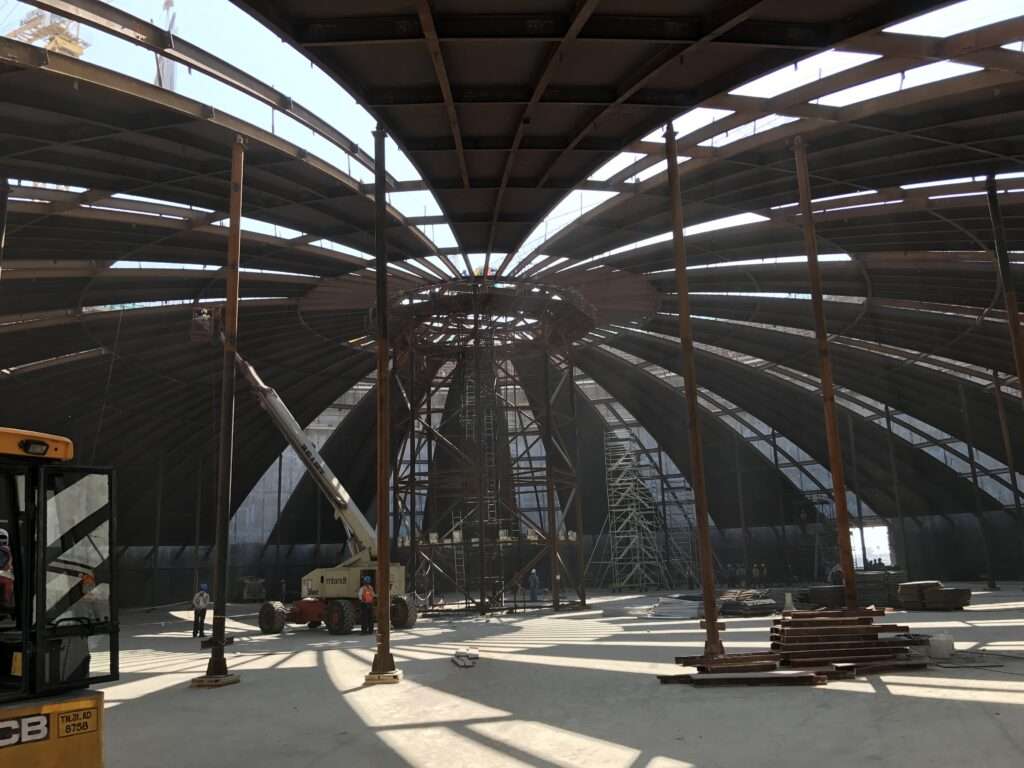

10 – Inner view of tank – Rafter installation
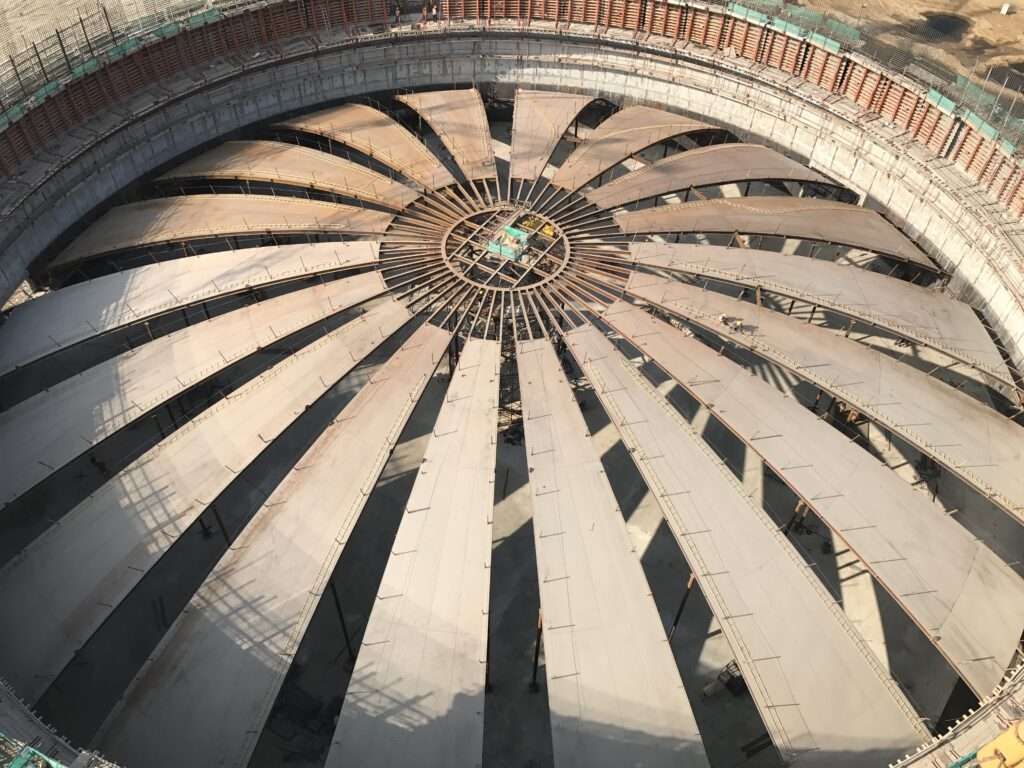

11 – Top view of Rafters
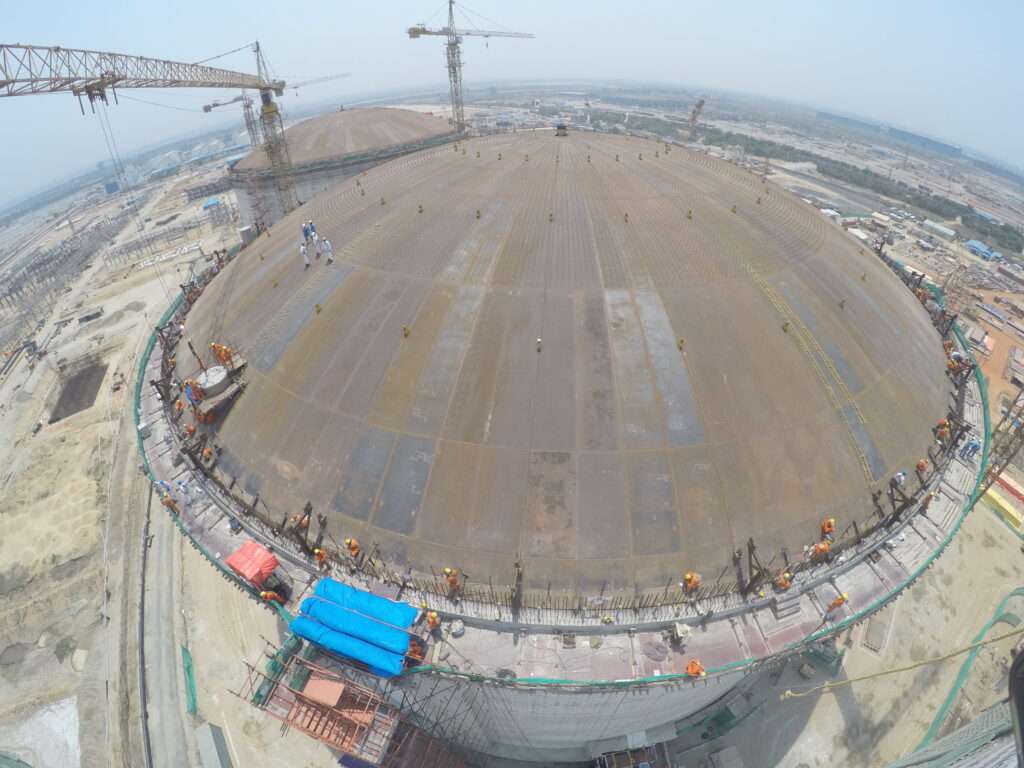

12 – After Roof Airlifting
- Concrete is placed above the steel roof.
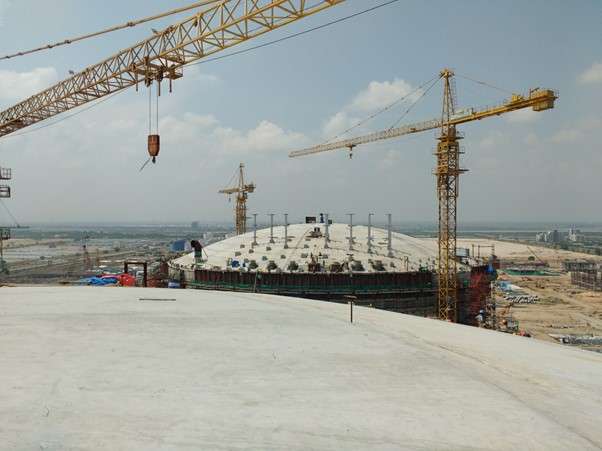

13 – Roof Concreting
Inner tank
- The inner tank is installed after the roof concrete is completed.
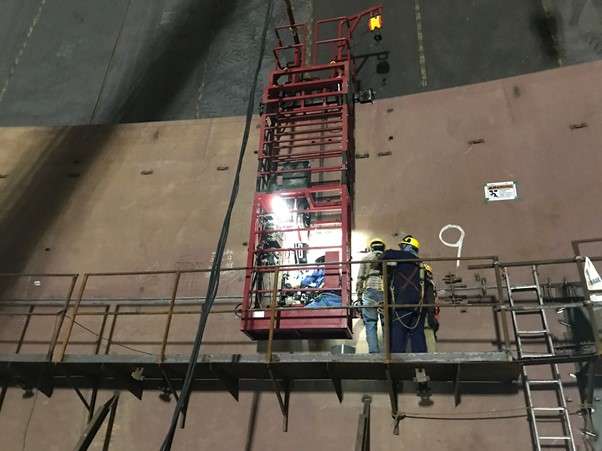

14 – Welding of Inner tank plate – 9% Nickel
- The material used for inner tank linings is 9% Nickel, as they can remain ductile and crack-resistant when exposed to extremely low temperatures.
Testing & commissioning
- Rigorous testing, including pressure and hydro tests, is conducted to verify the tank’s integrity and safety.
Commencement of operations
- Once the local regulatory and other approvals are obtained, the LNG tank is ready for service. It plays an important role in the LNG supply chain, aiding the storage and distribution of LNG to meet energy demands.
Conclusion:
LNG tanks are essential components in today’s energy industry and enable safe and efficient storage of natural gas. The process of construction, fabrication, and welding involves precision, adherence to safety standards, and rigorous quality control.
Choose Leopard Project Control as your construction scheduling company for your LNG tank project. Contact us today.





